Making a BigQuery Connection
This article covers:
- How to set up a connection to a BigQuery database
- How to add datasets
- How to do connection overrides on a BigQuery connection
- The supported BigQuery data types and the respective Luzmo data type they are mapped to
1. How to setup a BigQuery connection
First you need setup a service account to access BigQuery:
Go to Google Cloud Console and select
IAM & admintab from the left menu. Click onService accountsfrom the list.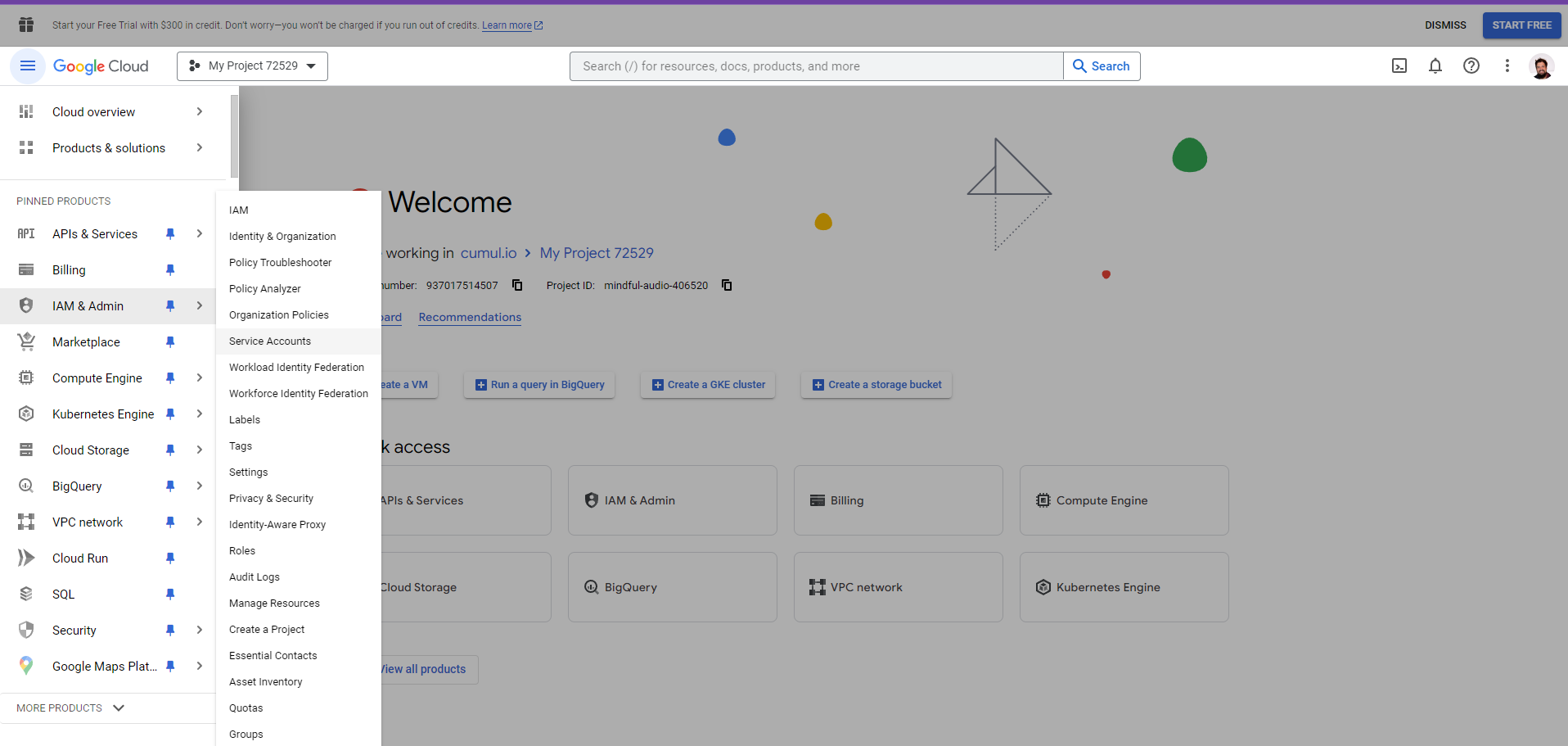
Click
Create new service accountand give it a name of your choice (eg. Luzmo Connector). SelectBigQuery Connection User,BigQuery Job User,BigQuery Metadata ViewerandBigQuery Data Viewerfrom the role drop down.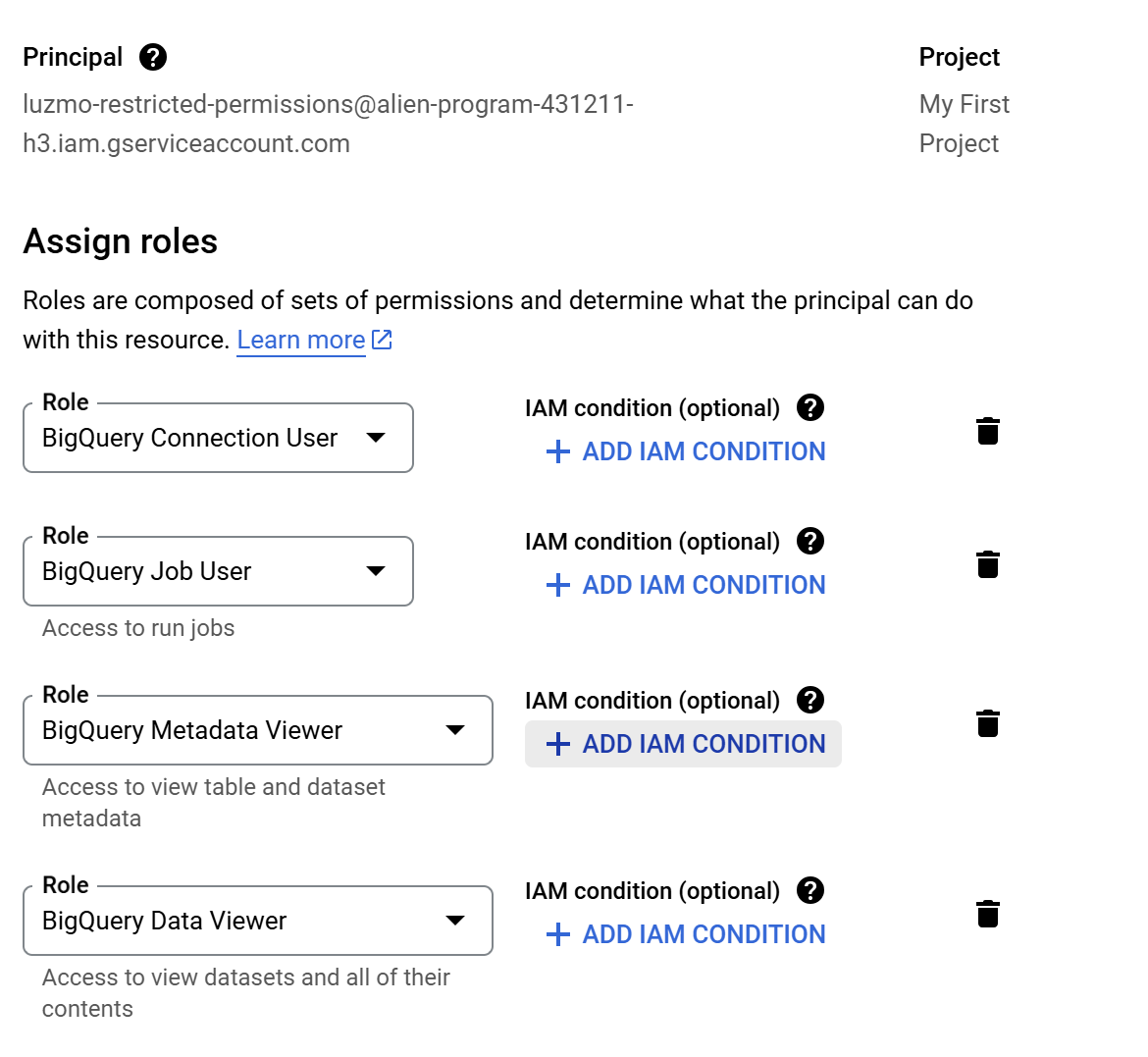
Create a new "key".
Once created, you can then download a JSON with the credentials (the following example is not a valid key)

Navigate to the Connections page, select New Connection, then select the BigQuery from the New Connection modal. You'll be asked to provide a key and token. Copy these verbatim from the JSON file:
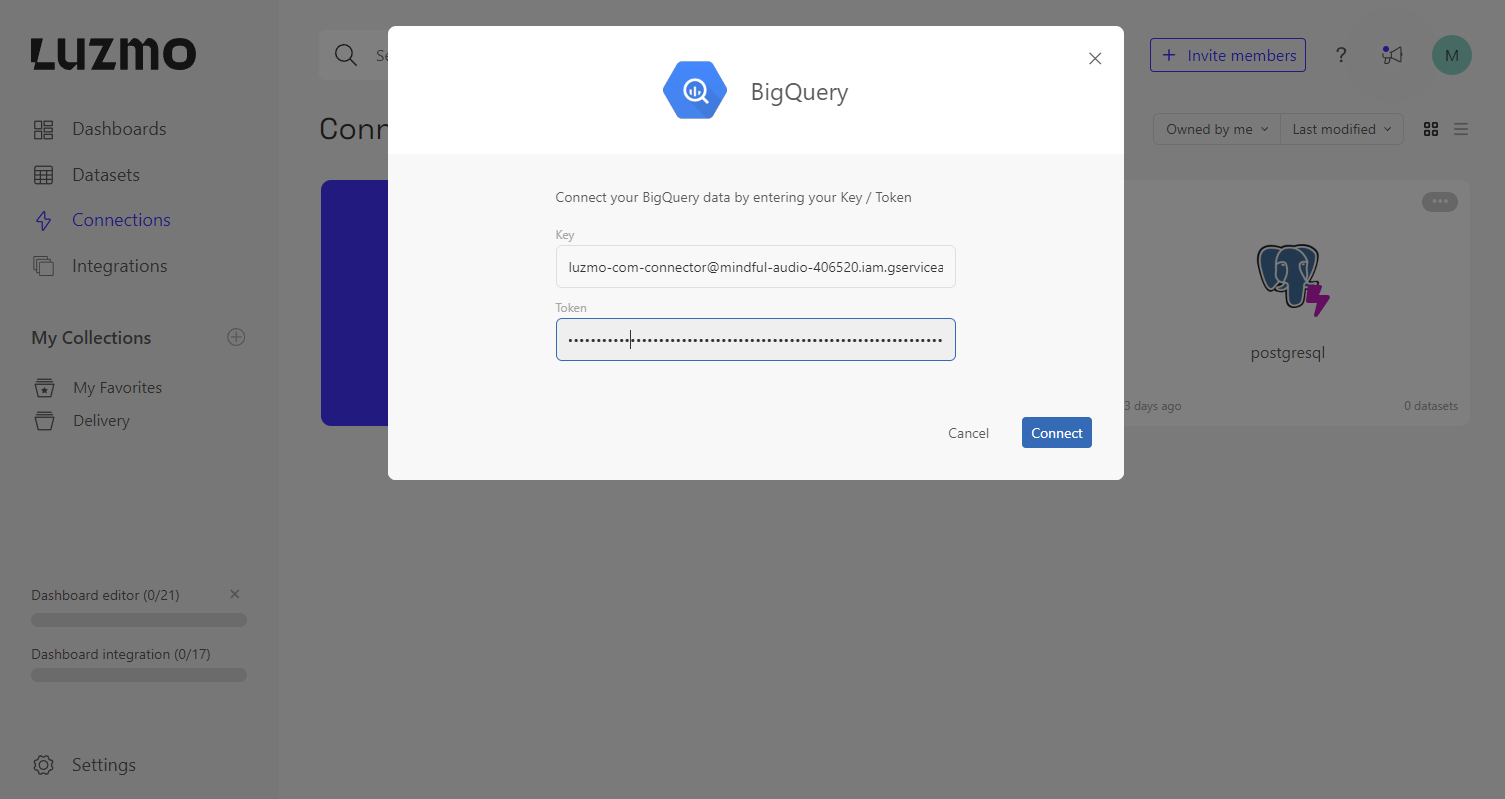
- Copy the value of JSON field
client-emailas key - Copy the value of JSON field
private-keyas token
- Copy the value of JSON field
Please refer to the examples in our developer documentation to find out how to create a connection to BigQuery via our API.
Notes: To ensure that e.g. only the Luzmo application can access your Bigquery instance, it is highly recommended to whitelist Luzmo's range of static IP addresses. You should whitelist Luzmo's range of IP addresses as described here.
2. How to add datasets
Once you have connected your BigQuery you can add datasets as explained here.
- You can select one or multiple datasets as available in your BigQuery and link them in Luzmo to ensure they can be used together in a dashboard.
- You can also add SQL datasets by switching to the SQL tab in the dataset creation modal. While creating or editing a SQL dataset, you can parameterize anything within the query by specifying
{{metadata.< parameter name >|< default value >}}. Find out more about parameterized SQL Datasets.
Also make sure to check out this article on Preparing your data for analytics.
To find out how to add datasets using our API, please refer to the examples in our developer documentation.
3. Bigquery Connection Overrides
When generating an Authorization token to grant a user acces to your embedded dashboards it is possible to override the data source properties in the authorization request to dynamically use different properties. Find out more about connection overrides.
The fields available for overriding a Bigquery connection are as follows:
- Connection ID: The ID of the Connection to be overridden. Retrieve the ID to specify as detailed here.
- key: The new IAM Service account 'client-email'.
- token: The new IAM Service account 'private-key'. Make sure to escape newline
\ncharacters in the token (i.e.\\n) - datasets: List of dataset-level overrides. Useful if you want to override only a single dataset in your dashboard or if you have a separate table per client. The SQL query of the dataset can also be overridden if it's a SQL dataset within Luzmo.
- schema: A concatenation of a Bigquery project and dataset identifier, separated by a colon ':' (i.e.
bigquery_project_id:bigquery_dataset). - table: The new Bigquery table to query.
- sql: The new SQL query to run (only for SQL datasets). Alternatively, you could also use parameterized SQL Datasets.
- schema: A concatenation of a Bigquery project and dataset identifier, separated by a colon ':' (i.e.
Our developer documentation has more info about connection overrides and an examples of Bigquery connection overrides.
Example code demonstrating how to dynamically override a Bigquery connection to use a different Bigquery IAM service account when embedding:
import Luzmo from '@luzmo/nodejs-sdk';
const client = new Luzmo({
api_key: '<your Luzmo API key>',
api_token: '<your Luzmo API token>',
host: 'https://api.luzmo.com:443'
});
const response = await client.create('authorization',
{
type: "embed",
username: "< A unique and immutable identifier for your user >",
name: "< user name >",
email: "< user email >",
suborganization: "< a suborganization name >",
access: {
collections: [
{
id: "<collection_id>",
inheritRights: "use"
}
]
},
account_overrides: {
<your connection_id>: {
key: "new-email@test.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
token: "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- <obfuscated> -----\nEND PRIVATE KEY-----"
}
}
}
);
Example code demonstrating how to override the SQL query for a single Bigquery SQL dataset:
import Luzmo from '@luzmo/nodejs-sdk';
const client = new Luzmo({
api_key: '<your Luzmo API key>',
api_token: '<your Luzmo API token>',
host: 'https://api.luzmo.com:443'
});
const response = await client.create('authorization',
{
type: "embed",
username: "< A unique and immutable identifier for your user >",
name: "< user name >",
email: "< user email >",
suborganization: "< a suborganization name >",
access: {
collections: [
{
id: "<collection_id>",
inheritRights: "use"
}
]
},
account_overrides: {
<your connection_id>: {
datasets: {
< Luzmo dataset ID >: {
sql: "SELECT ... FROM ..."
}
}
}
}
}
);
4. Supported Data Types
| Data Type in Big Query | Data Type in Luzmo |
|---|---|
| BOOL | hierarchy |
| BOOLEAN | hierarchy |
| STRING | hierarchy |
| BYTES | hierarchy |
| TIME | hierarchy |
| NUMERIC | numeric |
| DECIMAL | numeric |
| BIGNUMERIC | numeric |
| BIGDECIMAL | numeric |
| INTEGER | numeric |
| INT64 | numeric |
| FLOAT64 | numeric |
| FLOAT | numeric |
| DATE | datetime |
| DATETIME | datetime |
| TIMESTAMP | datetime |